 Dr. Glauser is an emergency physician at MetroHealth Medical Center, Cleveland, Ohio and professor of emergency medicine at Case Western Reserve University.
Dr. Glauser is an emergency physician at MetroHealth Medical Center, Cleveland, Ohio and professor of emergency medicine at Case Western Reserve University.
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: Vol 43 – No 06 – June 2024References
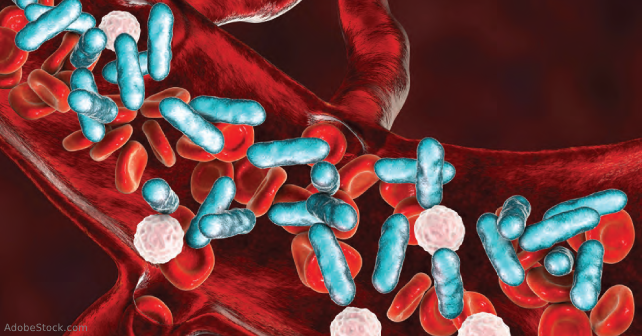
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2020;395(10219):200-211.
- Kumar A, Roberts D, Wood KE, et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2006;34(6):1589-1596.
- Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(19):1368-1377.
- Arina P, Singer M. Pathophysiology of sepsis. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(2):77-84.
- King J, Chenoweth CE, England PC, et al. Early Recognition and Initial Management of Sepsis in Adult Patients [Internet]. Ann Arbor, Mich.: Michigan Medicine University of Michigan; 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK598311/.
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315(8):801-810.
- Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med. 2021;49(11)e1063-e1143.
- Schertz AR, Lenoir KM, Bertoni AG, et al. Sepsis prediction model for determining sepsis vs SIRS, qSOFA, and SOFA. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(8):e2329729.
- Hernández G, Ospina-Tascón GA, Damiani LP, et al. Effect of a resuscitation strategy targeting peripheral perfusion status vs serum lactate levels on 28-day mortality among patients with septic shock: the ANDROMEDA-SHOCK randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019;321(7):654-664.
- Spiegel R, Farkas JD, Rola P, et al. The 2018 surviving sepsis campaign’s treatment bundle: when guidelines outpace the evidence supporting their use. Ann Emerg Med. 2019;73(4):356-358.
- Shapiro NI, Douglas IS, Brower RG, et al. Early restrictive or liberal fluid management for sepsis-induced hypotension (CLOVERS). N Engl J Med. 2023;388(6):499-510.
- Ferrer R, Martin-Loeches I, Phillips G, et al. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit Care Med. 2014;42(8):1749-1755.
- Peltan ID, Brown SM, Bledsoe JR, et al. ED door-to-antibiotic time and long-term mortality in sepsis. Chest. 2019;155(5):938-946.
- Permpikul C, Tongyoo S, Viarasilpa T, et al. Early use of norepinephrine in septic shock resuscitation (CENSER). A randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;199(9):1097-1105.
- Srzić I, Nesek Adam V, Tunjić Pejak D. Sepsis definition: What‘s new in the treatment guidelines. Acta Clin Croat. 2022;61(Suppl 1):67-72.
- Keh D, Trips E, Marx G, et al. Effect of hydrocortisone on development of shock among patients with severe sepsis: The HYPRESS randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;316(17):1775-1785.
- Lamontagne F, Masse MH, Menard J, et al. Intravenous vitamin C in adults with sepsis in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(25):2387-2398.
- Caironi P, Tognoni G, Masson S, et al. Albumin replacement in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(15):1412-1421.
- Ranieri VM, Thompson BT, Barie PS, et al. Drotrecogin alfa (activated) in adults with septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(22):2055-2064.
- Helwani MA, Lim A. Is venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation an option for managing septic shock. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2023;36(1):45-49.




One Response to “Updates in the Management of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock”
July 1, 2024
Joseph R Shiber, MDDear ACEPNow Editor,
Excellent synopsis of ED treatment of septic shock but I would like to add a few clarifications. The preferred balanced IVF is Plasmalyte-A since LR is somewhat hypotonic (Na 130) and uses lactate as a buffer, compared to acetate and gluconate in Plasmalyte-A (Na 140). The additional lactate is not actually detrimental to cellular activity but can hamper the usefulness of tracking lactate levels especially with hepatic or mitochondrial dysfunction where lactate is not being converted back to pyruvate for preparation to enter the TCA cycle. The optimal vasopressor for septic shock should correct the hemodynamic disorder(s) causing the tissue hypoxia. Levophed is certainly the most useful to help restore vascular tone (alpha effect) in the low SVR vasodilatory state of distributive shock while supplying a small B1-2 effect but there are cases where an inappropriate heart-rate response occurs (HR <80) due to medications (such as AVN blockers) or to intrinsic chronotropic failure (age or sepsis related). In these cases, it is paramount to address the heart rate at the same time, since if the heart rate remains inappropriately low while simply increasing SVR the cardiac output and tissue perfusion will potentially go down not up. Lastly, although ECMO is well recognized as a rescue for ARDS (V-V) and circulatory shock (V-A) it should be noted that active bacteremia or fungemia is a contraindication since the circuit will be contaminated immediately and cannot be sterilized.
Respectfully,
Joseph Shiber, MD, FACEP, FACP, FNCS, FCCM