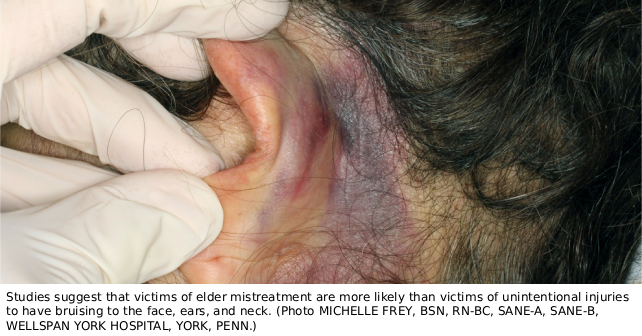
An 84-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by her daughter for bruising to the left ear. The patient’s daughter states that she noted this injury when she picked her mother up at her brother’s house, where the patient usually resides. The patient has a history of dementia and cannot recall how the injury occurred.
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: November 2025Introduction
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines five types of elder abuse:1
- Physical abuse is illness, injury, functional impairment, or death resulting from the intentional use of physical force. Examples include hitting, kicking, or pushing.
- Sexual abuse is forced or unwanted sexual interaction. Examples include unwanted sexual contact or penetration or non-contact acts, such as sexual harassment.
- Emotional or psychological abuse refers to verbal or nonverbal behaviors that inflict anguish, fear, or distress. Examples include humiliation, threats, or harassment.
- Neglect is the failure to meet an older adult’s basic needs. These needs include food, water, shelter, clothing, hygiene, and essential medical care.
- Financial abuse is the illegal, unauthorized, or improper use of money, benefits, property, or assets for the benefit of someone other than the older adult.
It is difficult to determine the prevalence of elder abuse. In one study, it was found that one in 10 elders were victims of elder mistreatment.2 It is estimated that for every one case of elder abuse, neglect, exploitation, or self-neglect reported to authorities, about five more go unreported.3 A study in New York found that for every case made known to programs and agencies, 24 were not reported.4 Although physical abuse is less common than psychological abuse or neglect, victims of physical abuse are more likely to present to emergency departments or urgent care facilities. Emergency physicians are in a unique position to recognize and intervene in cases of elder mistreatment.
Patterns of Injury
To identify nonaccidental trauma (NAT) in elderly patients, emergency physicians must recognize the patterns of injury that are more common in cases of NAT than in accidental injury. This can be difficult due to normal physiologic changes of aging. There are, however, some red flags suggesting NAT. They include:
- Injuries inconsistent with reported mechanism or history;
- Delay in presentation;
- Multiple injuries at different stages of healing; and
- Specific patterns of injury more consistent with NAT than with accidental trauma.
Although research regarding patterns of injury in elder mistreatment isstill scarce, several studies have suggested that certain patterns of bruising are more common in NAT than in accidental trauma. Larger bruises (those greater than 5 cm in size) are more likely to be the result of abusive trauma.5 Victims of elder mistreatment are more likely than victims of unintentional injuries to have bruising to the face, ears, and neck. They are more likely to have injuries to the upper extremities and the torso, particularly the back.5,6,7 Injuries to the lateral and anterior upper arms are also common.8 Patterned injuries (wounds that reproduce the distinctive shape, size, or characteristics of the objects that caused them) are also more common in NAT.
Pages: 1 2 3 | Single Page



No Responses to “Patterns of Injury in Elder Abuse”