Figure 1: The SPG is associated with the trigeminal nerve, the major nerve involved in headache disorders. It is an extracranial parasympathetic ganglion located behind the nasal bony structures. It has two ganglia, one in each of the bilateral fossae located posterior to the middle turbinate. It is made up of three nerves, the sensory, sympathetic, and parasympathetic.
Figure 1: The SPG is associated with the trigeminal nerve, the major nerve involved in headache disorders. It is an extracranial parasympathetic ganglion located behind the nasal bony structures. It has two ganglia, one in each of the bilateral fossae located posterior to the middle turbinate. It is made up of three nerves, the sensory, sympathetic, and parasympathetic.
By Joseph Harrington
|
on May 14, 2018
|
0 Comment

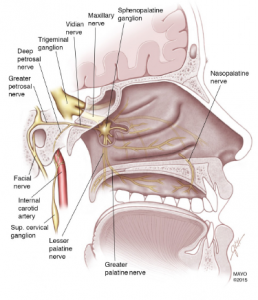

No Responses to “Figure 1: The SPG is associated with the trigeminal nerve, the major nerve involved in headache disorders. It is an extracranial parasympathetic ganglion located behind the nasal bony structures. It has two ganglia, one in each of the bilateral fossae located posterior to the middle turbinate. It is made up of three nerves, the sensory, sympathetic, and parasympathetic.”