Patient Presentation
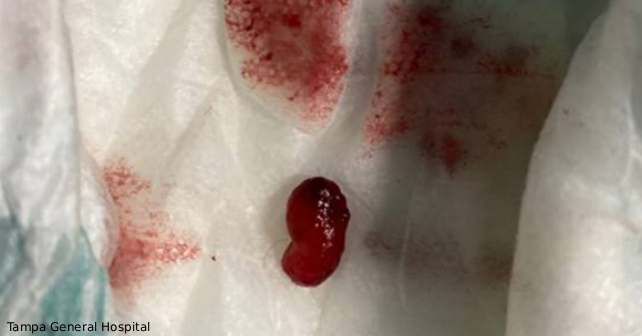
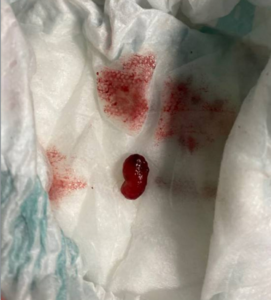
A 3-year-old female without past medical, surgical, or developmental history, and who is up to date on vaccines, presented with a chief complaint of “rectal prolapse” which occurred 20 minutes prior to arrival. She was in a normal state of health, eating and acting normally, until she attempted to have a bowel movement and developed abdominal and anal pain with a small amount of blood. The mother reported a protruding mass on wiping. The child was toilet training and had episodes of stool retention previously but had a formed bowel movement earlier in the day. There have been no recent illnesses or vaccinations, changes in diet, travel, sick contacts, fevers, upper respiratory symptoms, vomiting, diarrhea, or rashes. Her mother had a history of celiac disease, but denied family history of polyposis disorders, inflammatory bowel disease, or colon cancer. On arrival, the child’s vital signs were normal, weight was in the 21st percentile (higher than one year prior), she was nontoxic appearing, and in no acute distress. She was holding her knees to her chest and appeared uncomfortable. Her abdomen was soft, nontender, nondistended, with active bowel sounds. Her external anal exam appeared normal, without fissures or hemorrhoids, but her diaper had a bean-shaped mass of mucosal tissue with streaks of blood.
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: January 2026Diagnosis and Management
The initial differential diagnoses for the patient included thrombosed hemorrhoids, anal fissures, Meckel’s diverticulum, intussusception, infective enterocolitis, proctitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and proctitis. While the “mass in the diaper” seemed to have mucosal tissue qualities, it was unclear whether the source was from the patient or partially undigested food product. Shortly after initial evaluation, the patient had a bowel movement in the department with frank blood; her pain subsequently resolved afterwards without further intervention.
Evaluation included an ultrasound for intussusception that showed no abnormal findings. KUB X-ray showed an abnormal appearance of the distal descending colon, raising the possibility of bowel wall thickening, possibly infectious or inflammatory in etiology, and moderate stool in the ascending colon. Pediatric gastroenterology (GI) was consulted and recommended obtaining labs including CBC, CMP, coagulation studies, and tissue transglutaminase IgA – all of which were within normal range. She was monitored in the department and repeat bowel movement was without any bleeding or pain. She tolerated oral intake, her vitals remained normal, and she was ultimately discharged home to follow up with her primary care and pediatric GI. The tissue sample was sent for pathology which resulted two days later as a polypoid fragment of granulation tissue with dilated colonic glands and inflammation, consistent with inflammatory/juvenile polyp, negative for dysplasia. She followed up with her pediatrician two days later without recurrence of symptoms and a normal exam. She was seen by pediatric GI 19 days after her emergency department visit without any recurrence of symptoms, abnormal findings on exam, and no additional imaging or colonoscopy was recommended. The exact cause of this patient’s symptoms is still unclear, but it is likely that the polyp and possibly some portion of the rectum prolapsed, strangulated and amputated, leaving a bleeding stump that spontaneously achieved hemostasis.
Pages: 1 2 3 | Single Page




No Responses to “Case Report: A Pediatric Amputated Juvenile Polyp”