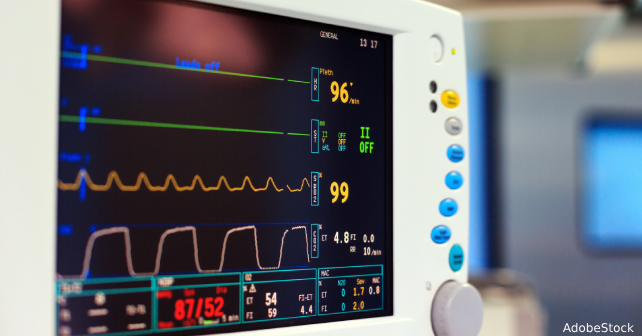
The treatment of toxic exposures causing hemodynamic instability can represent a unique clinical challenge in the ED. In general, the mainstay of treatment includes decontamination followed by reversal agents if available. While these are being prepared, or in cases where they do not exist, supportive care is paramount.
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: July 2025For hypotension, fluid resuscitation followed by the initiation of vasopressors is the mainstay. Consider and manage sodium blockade and QT prolongation in the case of cardiac dysrhythmias, such as those that develop in tricyclic antidepressant overdose. Finally, consider adjunctive therapy such as high-dose insulin therapy or lipid emulsion for beta blocker or calcium channel blocker toxicity. In the most severe of cases, VA ECMO may be considered. All these treatments are best utilized in conjunction with a medical toxicologist, when available, or by calling the national poison control network at 1-800-222-1222.
 Dr. Shah is a PGY-3 resident at Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center.
Dr. Shah is a PGY-3 resident at Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center.
 Dr. Johnson is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at the Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center and College of Medicine.
Dr. Johnson is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at the Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center and College of Medicine.
References
- Smollin C. Poisoning or Overdose–Related Hypotension. In: Papadakis MA, McPhee SJ, Rabow MW, Mc- Quaid KR, Gandhi M. eds. Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment 2024. McGraw-Hill Education; 2024.
- Alshaya OA, Alhamed A, Althewaibi S, et al. Calcium channel blocker toxicity: a practical approach. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2022;15:1851-1862.
- Khalid MM, Galuska MA, Hamilton RJ. Beta-blocker toxicity. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; July 28, 2023.
- Ollier M, Giles S, Gosselin S. The occasional intralipid emulsion therapy. Can J Rural Med. 2023;28(4):195- 200.
- Kaiser SK, Dart RC. The roles of antidotes in emergency situations. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2022;40(2):381-394.
- Walter E, McKinlay J, Corbett J, Kirk-Bayley J. Review of management in cardiotoxic overdose and efficacy of delayed intralipid use. J Intensive Care Soc. 2018;19(1):50-55.
- Upchurch C, Blumenberg A, Brodie D, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation use in poisoning: a narrative review with clinical recommendations. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2021;59(10):877-887.
- Wagner ML, Pergolizzi J Jr, LeQuang JAK, et al. From antidepressant tianeptine to street drug zaza: a narrative review. Cureus. 2023;15(6):e40688.
- Papudesi BN, Malayala SV, Regina AC. Xylazine Toxicity. 2023 Jul 17. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–.
- Agrawal S, Khazaeni B. Acetaminophen Toxicity. 2023 Jun 9. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–.
- Graham J, Traylor J. Cyanide Toxicity. 2023 Feb 13. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–.
- Hanley ME, Patel PH. Carbon Monoxide Toxicity. 2023 Jan 23. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–.
- Kuivenhoven M, Mason K. Arsenic Toxicity. 2023 Jun 12. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–.
Pages: 1 2 3 4 | Single Page



No Responses to “Toxin-Induced Hypotension Treatment Tips”