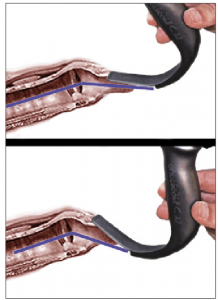
Figure 2 (Right). Schematic representation of the angle of approach. The top image shows ideal placement of a hyperangulated blade—in this case, a GlideScope Titanium blade—compared to overinsertion (bottom image). Note that the approach angle is more acute and that there is less room for tube delivery between the blade and the larynx.
Figure 2 (Right). Schematic representation of the angle of approach. The top image shows ideal placement of a hyperangulated blade—in this case, a GlideScope Titanium blade—compared to overinsertion (bottom image). Note that the approach angle is more acute and that there is less room for tube delivery between the blade and the larynx.
By Joseph Harrington
|
on December 15, 2015
|
0 Comment


No Responses to “Figure 2 (Right). Schematic representation of the angle of approach. The top image shows ideal placement of a hyperangulated blade—in this case, a GlideScope Titanium blade—compared to overinsertion (bottom image). Note that the approach angle is more acute and that there is less room for tube delivery between the blade and the larynx.”