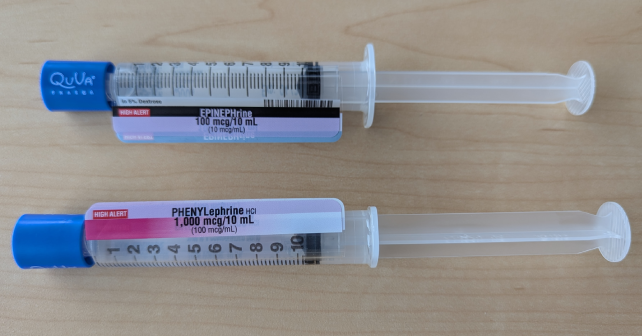
Over the last several years, I have seen a significant increase in the use of push-dose pressors in the ED. If you are not already doing so, hopefully, you can put these tips and tricks into action on your next shift!
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: June 2025 (Digital) Dr. Jansson is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Harvard Medical School and an emergency and critical care physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. He practices in both the ED and ICU.
Dr. Jansson is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Harvard Medical School and an emergency and critical care physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. He practices in both the ED and ICU.
References
- Holden D, Ramich J, Timm E, et al. Safety considerations and guideline-based safe use recommendations for “bolus-dose” vasopressors in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 2018;71(1):83-92.
- Tisdale JE, Patel R V, Webb CR, et al. Proarrhythmic effects of intravenous vasopressors. Vol. 29, Ann Pharmacother. 1995.
- Nawrocki PS, Poremba M, Lawner BJ. Push dose epinephrine use in the management of hypotension during critical care transport. Prehospital Emergency Care. 2020;24(2):188-195.
- Berkenbush M, Singh L, Sessa K, Saadi R. Scoping review: is push-dose norepinephrine a better choice? West J Emerg Med. 2024;25(5):708-714.
- Nowadly CD, Catlin JR, Fontenette RW. Push-dose vasopressin for hypotension in septic shock. J Emerg Med. 2020;58(2):313-316.
- Singer S, Pope H, Fuller BM, Gibson G. The safety and efficacy of push dose vasopressors in critically ill adults. Am J Emerg Med. 2022;61:137-142.
- Cole JB, Knack SK, Karl ER, et al. Human errors and adverse hemodynamic events related to “push dose pressors” in the emergency department. J Med Toxicol. 2019;15(4):276-286.
- Acquisto NM, Bodkin RP, Johnstone C. Medication errors with push dose pressors in the emergency department and intensive care units. Am J Emerg Med. 2017;35(12):1964-1965.
- Weingart S. Push-dose pressors for immediate blood pressure control. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2015;2(2):131-132.
- Weingart S. Push Dose Pressors. https://emcrit.org/wp-content/uploads/push-dose-pressors.pdf. Accessed March 5, 2025.
- Browning B. Push-Dose Pressors. https://www.emdocs.net/push-dose-pressors/. Published: January 4, 2014. Accessed June 3, 2025.
- Tilton LJ, Eginger KH. Utility of push-dose vasopressors for temporary treatment of hypotension in the emergency department. J Emerg Nurs. 2016;42(3):279-281.
- Tian DH, Smyth C, Keijzers G, et al. Safety of peripheral administration of vasopressor medications: a systematic review. Emerg Med Australas. 2020;32(2):220-227.
- Lewis T, Merchan C, Altshuler D, Papadopoulos J. Safety of the peripheral administration of vasopressor agents. J Intensive Care Med. 2019;34(1):26-33.
Pages: 1 2 3 | Single Page



2 Responses to “Push-Dose Pressors in the Emergency Department”
July 7, 2025
Seattle ER docGreat column. I’d love to see a follow up: what is the evidence that push dose pressors make a difference in patient outcomes?
We could just be treating numbers on a monitor, or maybe it’s actually helping the patient. Is there value in certain situations (e.g. EMS transport, bridging to pressor infusion in septic shock) but not in other situations (e.g. transient hypotension after intubation or procedural sedation)? A deep dive into the topic would be great.
December 29, 2025
Craig ButtonAs a nurse educator I really cringe when I see flushes being used to mix any medication. To many of the creators/influencers etc. have people mixing in a flush that is actually labeled for flush only and then they say label but don’t actual say what’s on the label.
The concept of push dose has been around for 25+ years. Was using it in SICU and in the OR forever it seems.