Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: Vol 34 – No 06 – June 2015(Click for larger image)
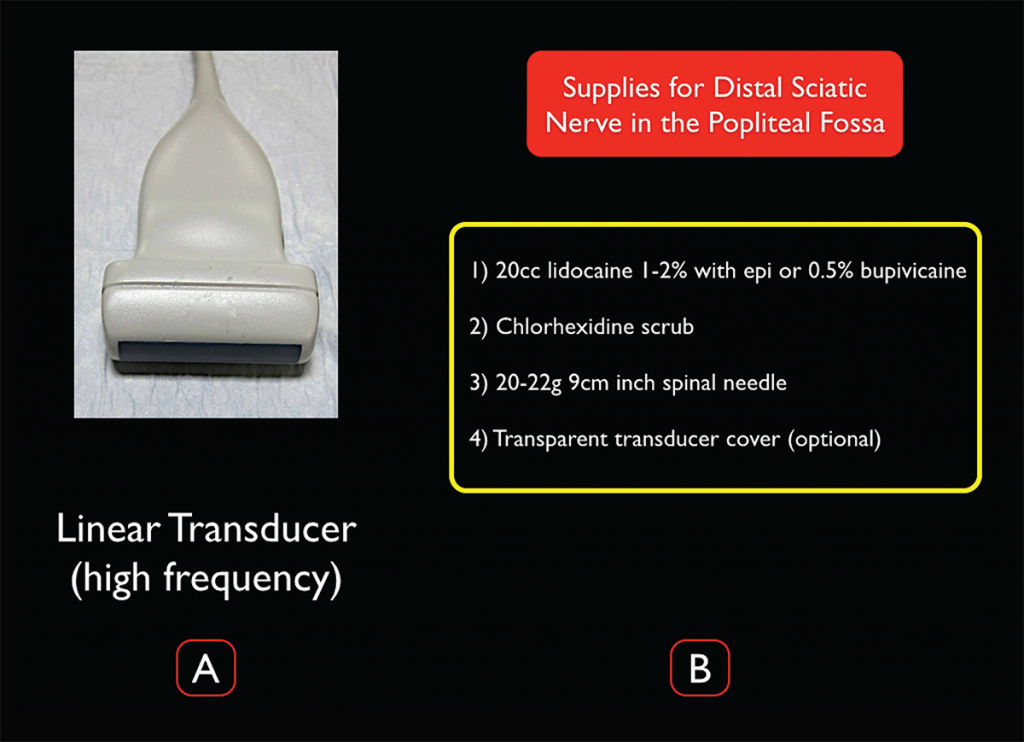
Figure 3. Transducer and supplies needed for ultrasound-guided distal sciatic nerve block in the popliteal fossa. Credit: Arun Nagdev
Survey Scan
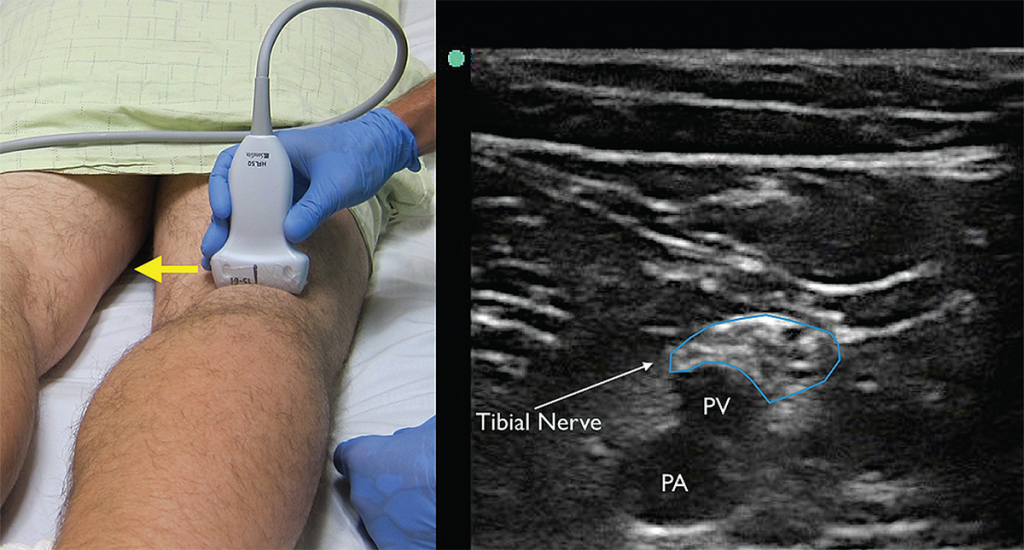
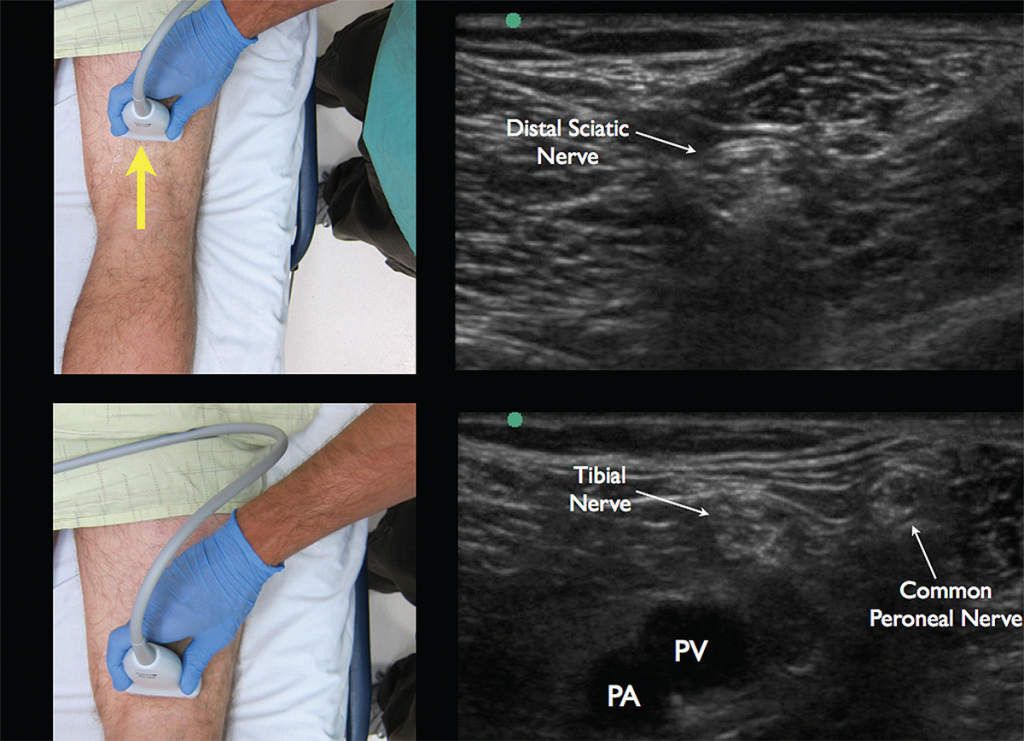
To prepare for the block, start by placing the high-frequency linear probe with the probe marker facing the patient’s right side at the popliteal crease and identify the popliteal artery and vein. The tibial nerve is commonly located just superficial to the popliteal vein and appears as a hyperechoic honeycomb-like structure (see Figure 4). If you are unable to locate the neural bundle, fan the probe caudal to cephalad to obtain the most perpendicular axis to the nerve, which allows for better visualization (an ultrasound phenomenon termed anisotropy). Once the tibial nerve is visualized, follow the nerve proximally until it joins with the common peroneal nerve (lateral) to form the distal sciatic nerve (see Figure 5). The operator should mark this location and note the depth of the nerve and distance from the lateral thigh to ensure the appropriate length of needle prior to starting the procedure.
(Click for larger image)
Figure 4. The tibial nerve sits just above the popliteal artery (PA) and popliteal vein (PV). Identification of this nerve is the first step in identifying the larger and more proximal distal sciatic nerve. Yellow arrow indicates direction of probe marker. Credit: Arun Nagdev
(Click for larger image)
Figure 5. Appropriate movement of the ultrasound probe cephalad to visualize the joining of the tibial nerve with the common peroneal nerve forming the distal sciatic nerve. Note the common peroneal nerve approaching from the lateral aspect. Credit: Arun Nagdev
Procedure
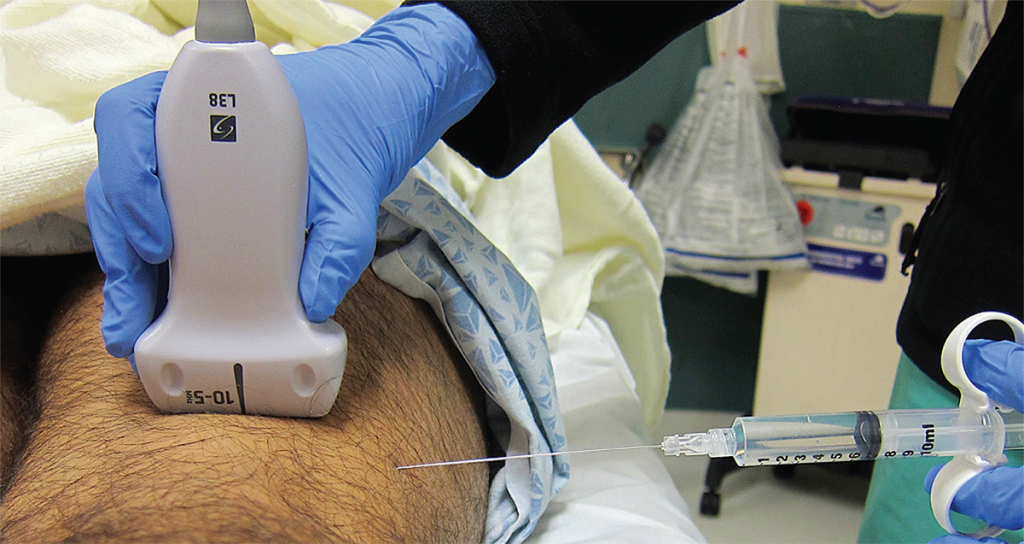
The distal sciatic nerve is often 2–4 cm under the skin surface, making for a steep needle angle if entering the skin just adjacent to the ultrasound transducer (like most other ultrasound-guided nerve blocks). Instead, we recommend measuring the depth of the nerve during the initial survey scan and entering the lateral leg with a flat angle to ensure clear needle visualization. After placing a small skin wheal (on the lateral aspect of the thigh), fill 20 mL of local anesthetic in a syringe attached to a 20–22 gauge, 3.5-inch (9 cm) spinal needle. The more lateral approach and depth of the distal sciatic nerve often necessitate the longer needle for an in-plane distal sciatic nerve block.
(Click for larger image)
Figure 6. Ultrasound and needle placement for the distal sciatic nerve block in the popliteal fossa. Note the flat needle entry lateral to the transducer. Credit: Arun Nagdev
Pages: 1 2 3 4 | Single Page




No Responses to “How to Perform Ultrasound-Guided Distal Sciatic Nerve Block in the Popliteal Fossa”